Ethernet Distance Limits: Can You Get Gigabit Beyond 100m?
The short answer is Yes, you can get Gigabit speeds beyond the standard 100-meter limit by using Ethernet extenders or fiber optic cables. The 100-meter Ethernet distance limit is one of the most frequently encountered challenges in network installations, especially for large facilities, security systems, and distributed office environments. While IEEE 802.3 standards strictly define this ethernet distance limit for copper-based networks, understanding why this limitation exists and how to work within or around it is crucial for successful network deployments. The 100m rule isn’t arbitrary – it’s based on precise electrical engineering principles involving signal attenuation, timing constraints, and power delivery requirements. For installers and network administrators in Kenya dealing with expansive commercial properties, industrial facilities, and residential compounds, knowing how to extend Ethernet networks beyond this limitation while maintaining gigabit speeds and reliability is essential for creating robust, scalable network infrastructure.
Standard Ethernet Distance Limits
The fundamental ethernet cable distance limit of 100 meters (328 feet) applies to all copper-based Ethernet standards, from Fast Ethernet (100 Mbps) to 10 Gigabit Ethernet. This distance represents the maximum cable length between active network devices, such as switches, routers, or network interface cards, and includes all patch cords and connections within the link. Here’s the ultimate gude to ethernet cables, if you want to make a decision on what ethernet cable to buy

Cat5eethernet cable : Supports Gigabit Ethernet (1000 Mbps) up to the full 100 meters. Cost-effective for standard installations.
Cat6 ethernet cable : Offers superior performance and better crosstalk resistance. Supports Gigabit Ethernet at 100 meters with greater reliability and is better for Power over Ethernet (PoE) over long distances.
Cat6a ethernet cable: The premium choice. Supports 10 Gigabit Ethernet over the full 100 meters and offers exceptional noise immunity, making it ideal for future high-speed network upgrades
The 100-meter specification is conservative, providing performance margins for various installation conditions, cable quality variations, and environmental factors. However, exceeding this limit progressively degrades signal quality and can result in complete link failure or intermittent connectivity issues.
Problems Beyond 100 Meters in Ethernet Cabling
When Ethernet cables exceed the standard 100-meter limit, several issues arise that impact performance and reliability:
- Signal Attenuation – As electrical signals travel through copper, resistance causes voltage loss. Over long runs, the signal weakens to the point where devices can’t reliably interpret data. Higher-speed protocols (like Gigabit or 10-Gigabit) are especially vulnerable.
- Timing Constraints – Ethernet relies on strict timing for collision detection, acknowledgments, and synchronization. Extra cable length adds propagation delays, which can cause errors in half-duplex networks and older Ethernet standards.
- Crosstalk & Interference – Longer distances increase exposure to electromagnetic noise from motors, fluorescent lights, or radio equipment. This interference couples into the cable, leading to data errors and slower speeds.
- Power Delivery in PoE – For Power over Ethernet (PoE), voltage drop becomes significant over long runs. Devices may receive insufficient power, especially with high-demand standards like PoE+ or PoE++, leading to malfunction or shutdown.
- Environmental Factors – Temperature swings alter cable resistance and capacitance, while moisture intrusion increases attenuation and creates new signal paths. Long runs are more exposed, making them prone to gradual performance loss.
How to Extend Ethernet Beyond 100m
| Solution | How It Works / Key Benefit |
| Network Switches | Extend Ethernet by segmenting every 100m; reliable, supports VLAN, QoS, and monitoring. |
| Ethernet Repeaters | Regenerate electrical signals for new 100m segments; simple but no advanced features. |
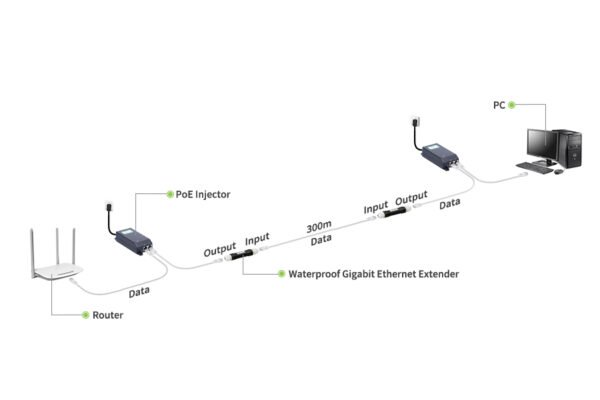
| PoE Extenders | Extend both data and power up to 200–500m; ideal for IP cameras and access points. |
| Media Converters | Convert copper to fiber; fiber spans from 2 km (multimode) to 40+ km (single-mode). |
| Powerline Networking | Uses existing electrical wiring for data; lower speed/reliability but good where cabling is impractical. |
| Wireless Bridges | Use RF links to span several km; require line-of-sight and may be weather-affected. |
Real-World Installations in Kenya
- Residential Compounds – Often exceed 100m when connecting IP cameras at gates and perimeters. Weatherproof switches extend coverage while maintaining gigabit speeds.
- Commercial Offices – Fiber backbones connect multiple buildings, while copper cabling handles internal runs. PoE extenders power access points in optimal locations.
- Industrial Facilities – Use shielded cables and repeaters to combat distance and interference, with fiber links ensuring reliable communication for critical systems.
- Educational Campuses – Structured cabling with hierarchical switching and fiber backbones provide scalable, future-ready network coverage.
- Agriculture – Outdoor-rated cables and PoE extenders enable smart farming systems like greenhouse monitoring, irrigation control, and livestock management.
Cost vs Performance Trade-offs in Extending Ethernet
When extending Ethernet beyond 100 meters, different solutions carry varying costs and performance outcomes in Kenya:
| Solution | Price in Kenya |
| Switch-Based Extension | KSh 20,000 – 80,000+ (managed/smart PoE switches) |
| PoE Extenders | KSh 2,000 – 7,000 (e.g., Hikvision ≈ KSh 7,000) |
| Fiber-Optic Solutions | Fiber: KSh 170 – 300+ per metre; Media converters: KSh 5,000 – 20,000+ |
| Repeaters / Extenders | KSh 2,000 – 3,500 (e.g., 4-port ≈ KSh 3,000) |
| Long-Term Costs | Adds 10–20% to material costs for professional installation |
Conclusion
Understanding ethernet distance limits and available extension methods enables successful network deployments regardless of physical constraints. While the 100-meter copper limitation is fundamental to Ethernet standards, modern extension technologies provide reliable solutions for virtually any distance requirement while maintaining gigabit performance.
The key to successful long-distance networking lies in selecting appropriate extension methods based on performance requirements, environmental conditions, and budget constraints. Whether using switches, extenders, or fiber solutions, proper planning ensures reliable connectivity that supports current needs while providing scalability for future growth.
Ready to extend your network beyond 100 meters? Browse long-run ethernet cables and accessories and get professional-grade solutions for distance extension. Our selection includes switches, PoE extenders, fiber converters, and specialized cables designed for reliable long-distance networking applications.


